Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scanner
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scanner
Siemens Magnetom Prisma (3 Tesla)
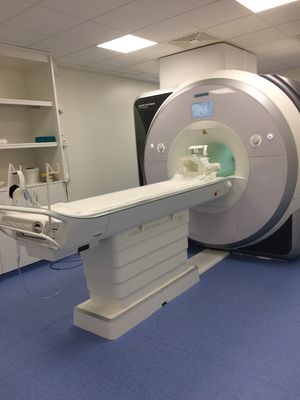
MRI stands for magnetic resonance imaging, also known as nuclear magnetic resonance imaging. fMRI stands for functional magnetic resonance imaging. These techniques allow us to examine the structure (MRI) and function (fMRI) of the brain. The procedure is non-invasive, meaning it is harmless to the human body (there are no side effects). The MR signals of water or other naturally occurring molecules are measured using strong magnetic fields to obtain images of body parts. fMRI can be used in a wide variety of ways to study functions and dysfunctions in various parts of the body. By recording a whole series of individual images while you perform a task in the MRI scanner, we can map your brain's activation during these tasks.
Methods
- Resting state
- Diffusion imaging (DTI)
- Spektroscopy
- Pharmacological fMRI
- Realtime fMRI / BCI
- Complex network analyses
- Source localization for MEG
- Patient studies
Peripheral devices
Headphones
Response Boxes
- Current Design (different options, including mouse)
Eyetracker
Projector
EEG
- 64-Kanal MR-kompatibles EEG
Custommade driving simulator
- steering wheel
- break and accelerator
